Measures the actual output of a solar power plant compared to its maximum potential output over a specific period. It indicates how effectively the plant converts available sunlight into electricity. A higher capacity factor signifies better performance and efficiency.
PV plant performance: challenges and solutions for large-scale solar projects


The global solar industry finds itself in an era of unprecedented scale, with global installations reaching nearly 600 GW in 2024—a 33% increase from the previous year.
This surge has pushed total global capacity past 2 TW, and forecasts suggest the world could be installing 1 TW of solar annually by 2030 to meet international climate goals.
This massive expansion of supply is met by a skyrocketing appetite for power. High-performance computing, particularly Artificial Intelligence (AI), is a primary driver, along with rapid electrification and increasing international policies to combat climate change.
For solar professionals, meeting this demand requires navigating hurdles across the entire project lifecycle, from selecting the ideal site to applying advanced O&M strategies to the finished power plant.
This guide explores the critical performance metrics and strategic engineering solutions needed to ensure the long-term technical and financial viability of today's large-scale energy assets.
Understanding PV plant performance
The performance of photovoltaic solar plants is evaluated using several key performance indicators (KPIs) that provide insights into their efficiency and reliability. Understanding these KPIs and the factors influencing them is crucial for optimizing the performance of solar energy plants.
Factors influencing PV plant performance
Several factors influence the performance of solar PV plants, including:
Location
The geographical location of a solar PV plant significantly affects its performance. Areas with high solar irradiance levels are ideal for maximizing energy generation. Factors such as latitude, altitude, and local climate conditions play crucial roles in determining the suitability of a location for a solar power plant.
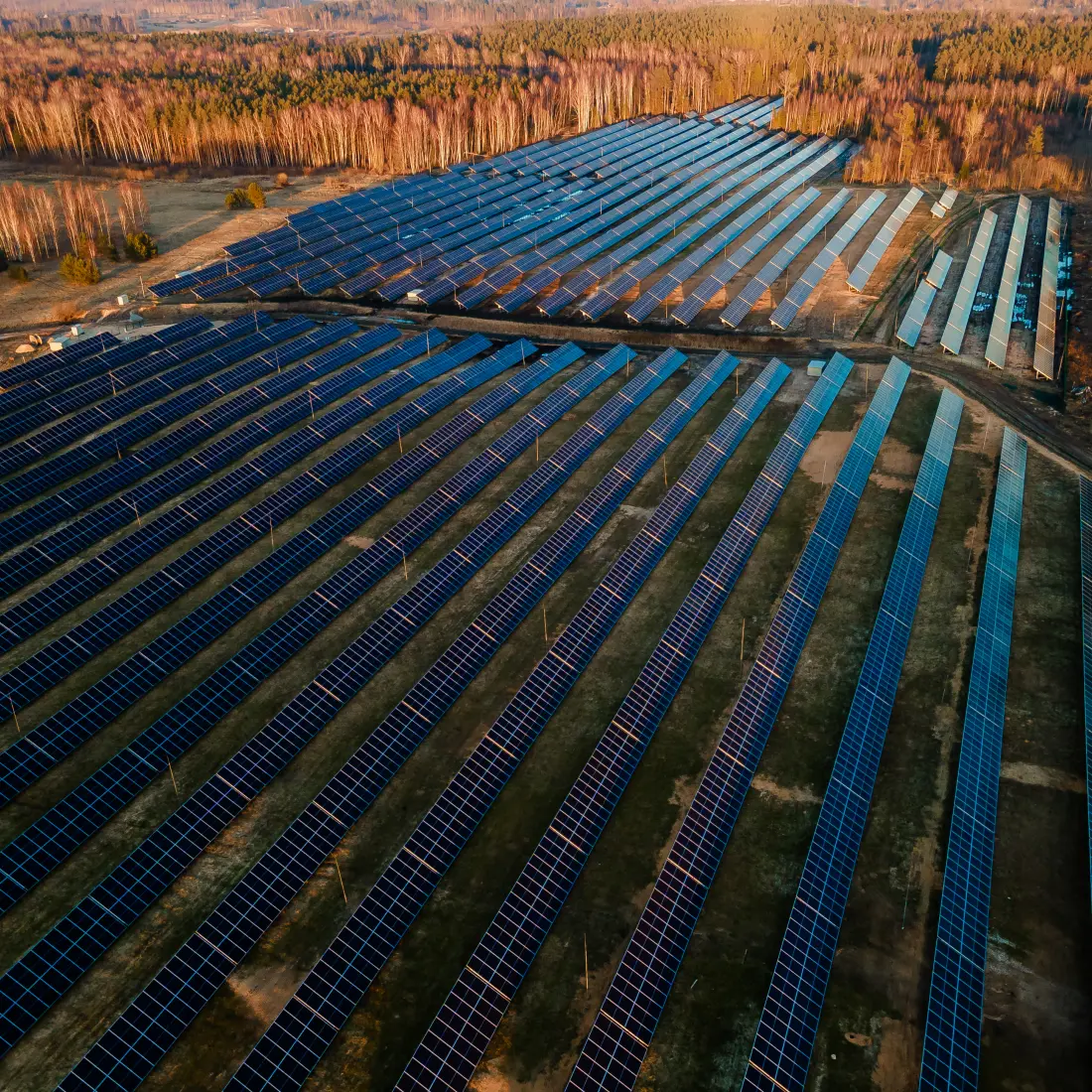

Design
The layout, orientation, and spacing of solar panels, among many other factors, are critical for optimizing sunlight capture and minimizing shading losses. Advanced solar design software tools and yield estimation software help engineers create efficient and effective solar plant designs.
Operational practices
Effective operations and maintenance (O&M) are essential for maintaining high performance. Regular cleaning of solar panels, timely repairs, and efficient monitoring systems contribute to the optimal operation of a solar PV plant. Predictive maintenance techniques using data analytics to forecast equipment failures can significantly enhance plant availability and reduce downtime.

In conclusion, by monitoring key performance indicators and addressing the factors influencing performance, solar energy plants can achieve their full potential and contribute significantly to the global transition to renewable energy.
Site selection and environmental considerations
The success of a large-scale solar PV plant begins with carefully selecting the site. Optimal site selection involves maximizing solar irradiance while minimizing shading and other obstacles. However, an increasingly congested power grid requires developers to evaluate land, connectivity, and grid capacity as an integrated framework rather than in isolation. This shift is essential to ensure projects can scale from megawatts to gigawatts without encountering late-stage bottlenecks.
Environmental impact assessments
Environmental impact assessments (EIAs) are conducted to evaluate the potential effects of a solar PV plant on the local environment. These assessments help identify and mitigate negative impacts, ensuring that the development of the solar plant is sustainable.
Soil erosion and land use
Solar installations can lead to soil erosion and changes in land use. Techniques such as terracing, vegetation cover, and erosion control measures, including solar site grading, are implemented to minimize these impacts.
Biodiversity and wildlife
Solar panel power plants can affect local ecosystems and wildlife habitats. EIAs identify sensitive areas and propose measures to protect biodiversity, such as creating buffer zones and wildlife corridors.
Mitigation strategies
To ensure sustainable development, several mitigation strategies are employed during the planning and construction phases of solar PV plants:
Effective site selection and environmental planning enhance the performance of solar PV plants and ensure their long-term viability and acceptance by local communities.
Design and engineering challenges
Designing large-scale PV power plants involves addressing several engineering challenges to ensure optimal performance and efficiency.
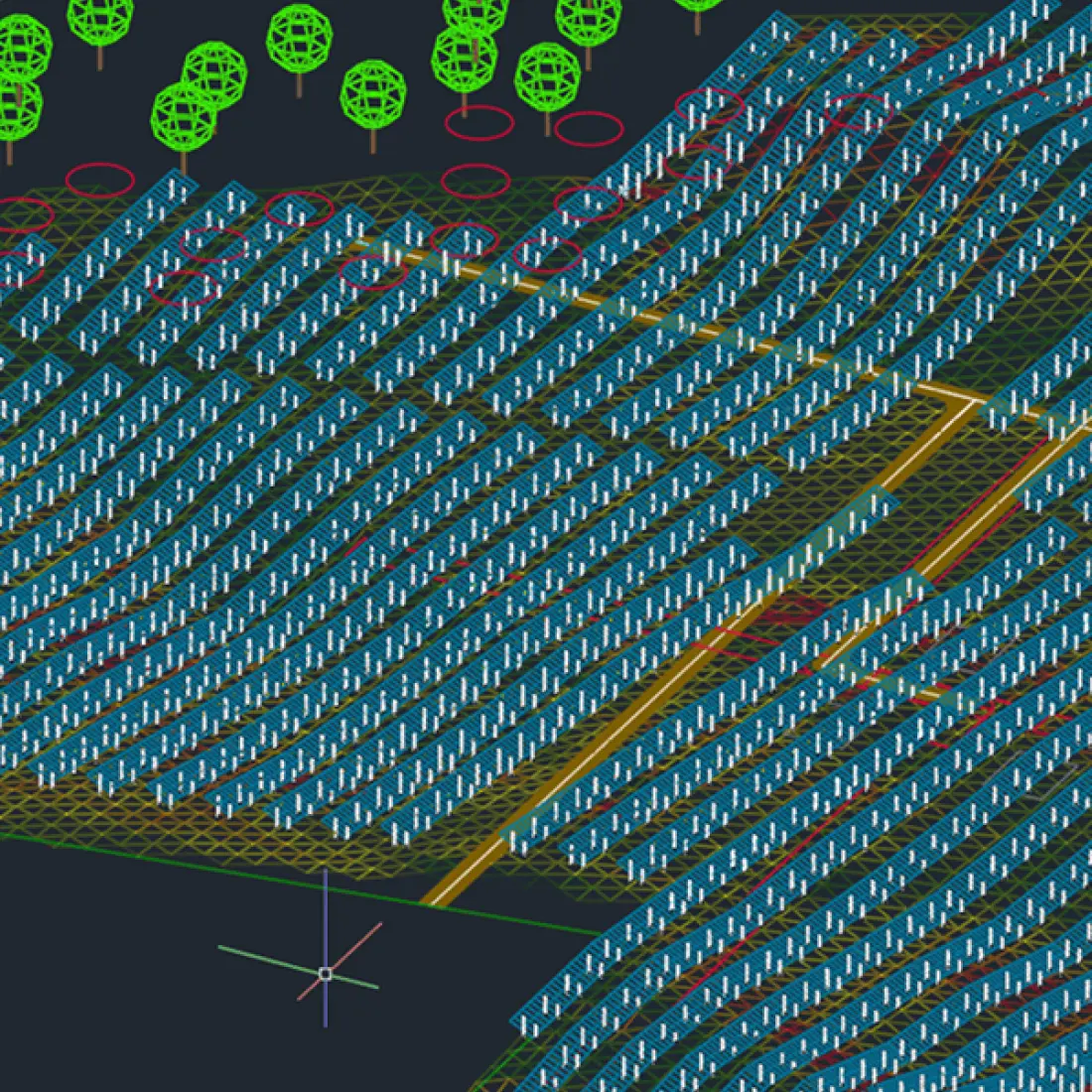
Terrain adaptation
PV plants are often built on diverse terrains, including flatlands, hills, and deserts. Each terrain type presents unique challenges that must be addressed to optimize performance. For instance, hilly terrains require careful planning to minimize shading and ensure even panel distribution.
Climate considerations
Different climates, such as arid deserts, humid tropics, and cold regions, affect the performance and longevity of solar panels. Dust and sand accumulation in deserts, humidity-induced corrosion in tropical areas, and snow cover in cold regions are some of the challenges that need specific design solutions.
Layout, orientation, and spacing optimization
Layout efficiency significantly impacts energy capture. Techniques like staggered rows and strategic spacing are used to minimize shading losses, while orientation and tilt are adjusted based on geographic location to ensure the array receives maximum sunlight throughout the day.
Solutions for optimizing layout, orientation, and spacing
Layout optimization
The arrangement of solar panels significantly impacts their efficiency. Techniques such as staggered rows, optimal tilt angles, and strategic spacing are used to maximize sunlight capture and minimize shading losses.
Orientation and tilt
The orientation and tilt of solar panels are adjusted based on the geographic location to capture maximum sunlight. For instance, in the northern hemisphere, panels are typically oriented towards the south to receive the most sunlight throughout the day.

Spacing and shading
Proper spacing between rows of panels prevents shading and allows for maintenance access. PVcase helps identify and mitigate shading issues, ensuring that each panel receives adequate sunlight.

High-fidelity performance simulation
Modern engineering requires detailed performance simulations that account for granular, hour-by-hour environmental data. By performing thermal-electrical modeling at the module level, engineers can create performance projections that reflect real-world operating conditions.
Iterative design
The path to a technically flawless design is rarely linear; it requires an iterative process where multiple design scenarios are compared side-by-side. Engineers must rank trade-offs between hardware costs and energy yield.
Operational and maintenance strategies
Effective operations and maintenance (O&M) are crucial for sustaining the performance and longevity of photovoltaic solar plants.
Proper O&M practices ensure that the solar panels and associated equipment operate at peak efficiency, minimizing downtime and maximizing energy production.
Importance of effective O&M practices
Sustaining performance
Regular maintenance activities, such as cleaning solar panels and inspecting electrical connections, help sustain the performance of PV power plants.
Reducing downtime
Proactive O&M practices reduce the risk of unexpected equipment failures, ensuring high availability and reliability. This involves routine inspections, predictive maintenance, and timely repairs.
Optimizing efficiency
Efficient O&M practices optimize the performance of solar panels and other components, leading to higher energy yields and better financial returns. This includes optimizing inverter settings, monitoring performance metrics, and implementing data-driven maintenance strategies.
Common O&M challenges
While O&M presents significant challenges, proper construction significantly reduces the risk of bumping into O&M-related challenges.
Grid integration and energy storage
Integrating large-scale PV plants into the electrical grid presents several challenges, primarily due to solar energy's intermittent nature. Let's have a closer look.
Challenges related to grid integration
Intermittency
Solar energy production is variable and depends on weather conditions and time of day. This intermittency challenges grid stability and reliability, as sudden fluctuations in solar output can affect grid operations.
Voltage stability
Large-scale integration of PV power plants can lead to voltage fluctuations in the grid. Maintaining voltage stability is crucial for preventing power quality issues and ensuring the smooth operation of electrical equipment.
Grid congestion
High penetration of solar energy can lead to congestion in certain areas of the grid, affecting the distribution and transmission of electricity. Managing this congestion requires advanced grid management techniques and infrastructure upgrades.
Solutions for an improved grid integration
Advanced inverter technologies
Modern inverters provide grid support functions such as voltage regulation, frequency control, and reactive power compensation.

Demand response strategies
Demand response involves adjusting the load on the grid in response to the availability of solar energy. This helps balance supply and demand, reducing the impact of solar intermittency on grid operations.

Battery energy storage systems (BESS)
Battery energy storage systems, such as batteries, store excess energy generated during peak sunlight hours and release it during periods of low solar production. This helps in smoothing out fluctuations in solar output and provides a reliable energy supply.

Financial and regulatory considerations
Large-scale solar PV plants' financial viability and regulatory compliance are critical factors that influence their development and operation.
Understanding the economic challenges and navigating the regulatory landscape is essential for successfully deploying solar energy projects.
Economic challenges
High initial capital costs
Developing large-scale PV plants requires substantial upfront investment. Costs include land acquisition, equipment procurement, construction, and grid connection.
Fluctuating energy prices
The volatility of energy prices affects the financial stability of solar PV projects.
Financial strategies
One of the best financial strategies in this case is Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs). PPAs are long-term contracts between a solar power producer and an electricity buyer. They provide revenue stability by securing fixed prices for the electricity generated over a specified period. PPAs are a common financing mechanism for large-scale solar projects, reducing financial risk and attracting investment.
Regulatory considerations
Compliance with standards
PV power plants must comply with local, national, and international standards and regulations. These include technical standards for equipment, safety protocols, and environmental guidelines.
Permitting and approvals
Obtaining permits and approvals from relevant authorities is a critical step in the development of PV projects. This process involves environmental assessments, land use approvals, and grid connection permits.
Grid connection requirements
Complying with grid connection requirements is essential for integrating solar plants into the electrical grid.
The PVcase solutions
PVcase offers an integrated solar project development platform designed to address the challenges faced by large-scale PV plants and ensure their optimal performance and efficiency.
PVcase Prospect
PVcase Prospect redefines scalable renewable site development with the best available interconnection and energy markets data, extensive land search, buildable area analysis, initial layouts, and portfolio management tools under one roof.
PVcase Ground Mount
PVcase Ground Mount is an AutoCAD-based solar design software for utility-scale solar power plants. It enables solar engineers to reduce project costs, boost reliability, and improve solar plant performance. Key features include:
Terrain-based PV layout generation
Automatically generates PV layouts tailored to specific terrains.

Piling and Collision Analysis
Identifies potential obstacles to help optimize and export piling data.
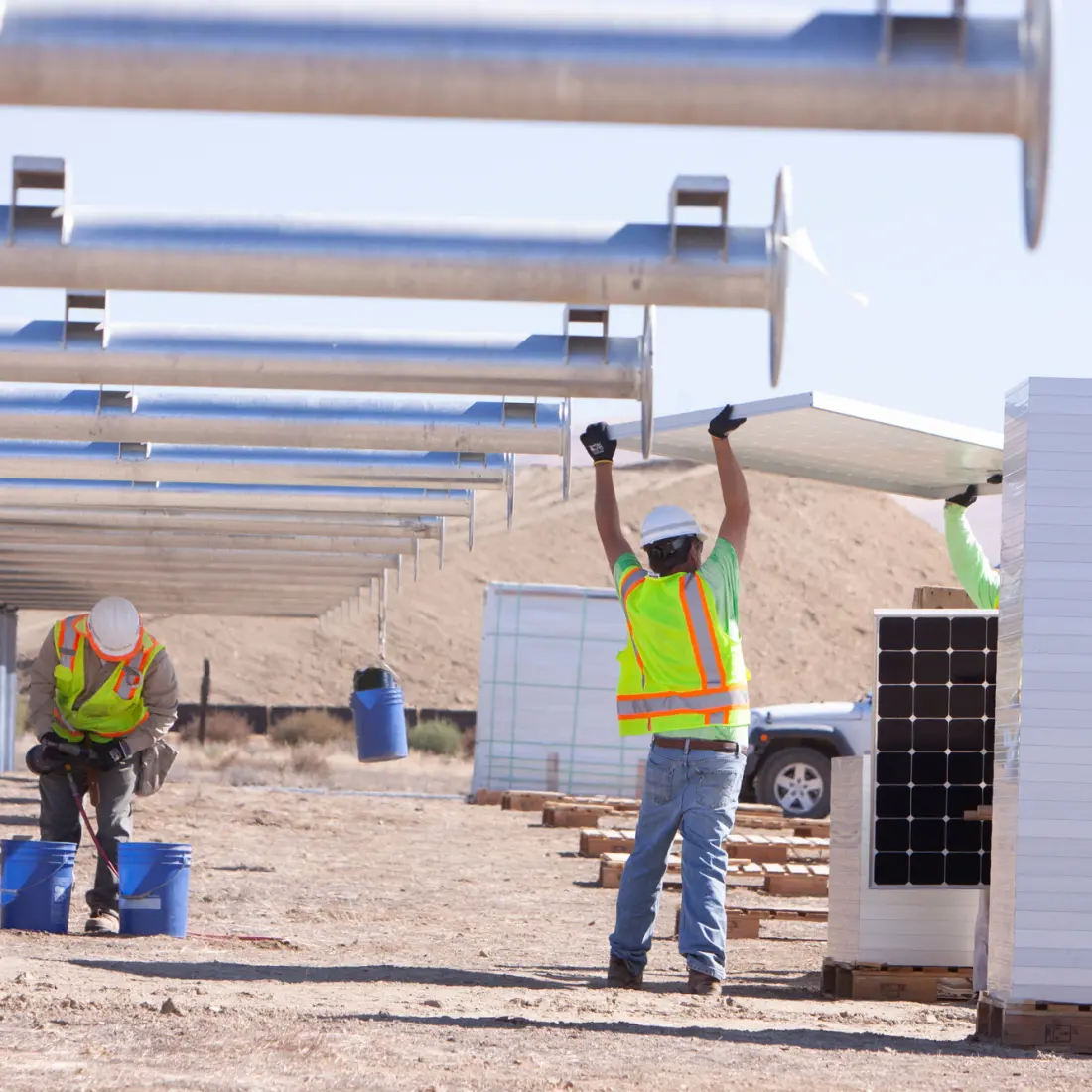

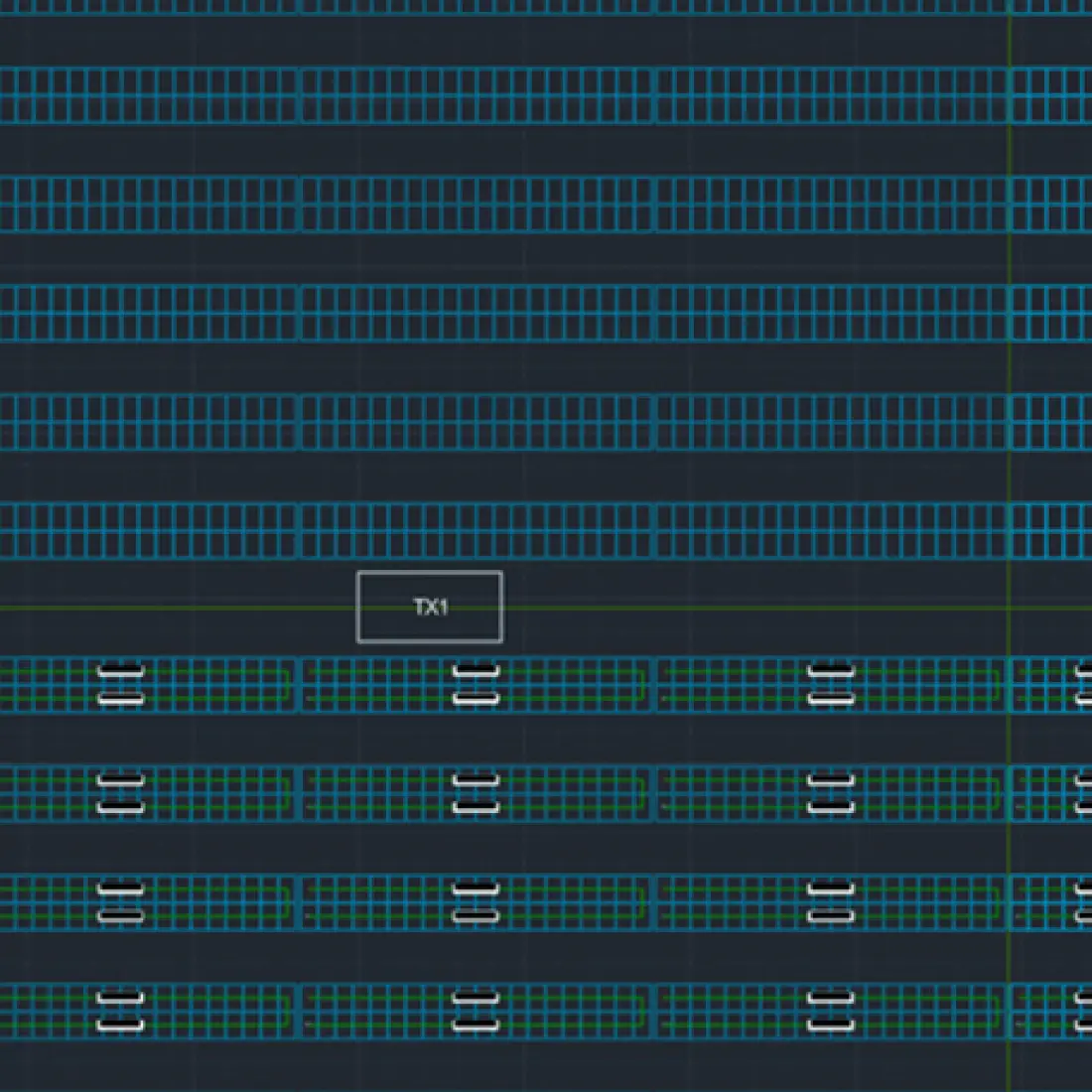
Electrical Device Placement and 3D Cabling
Enables precise placement of electrical components and comprehensive cabling visualization.
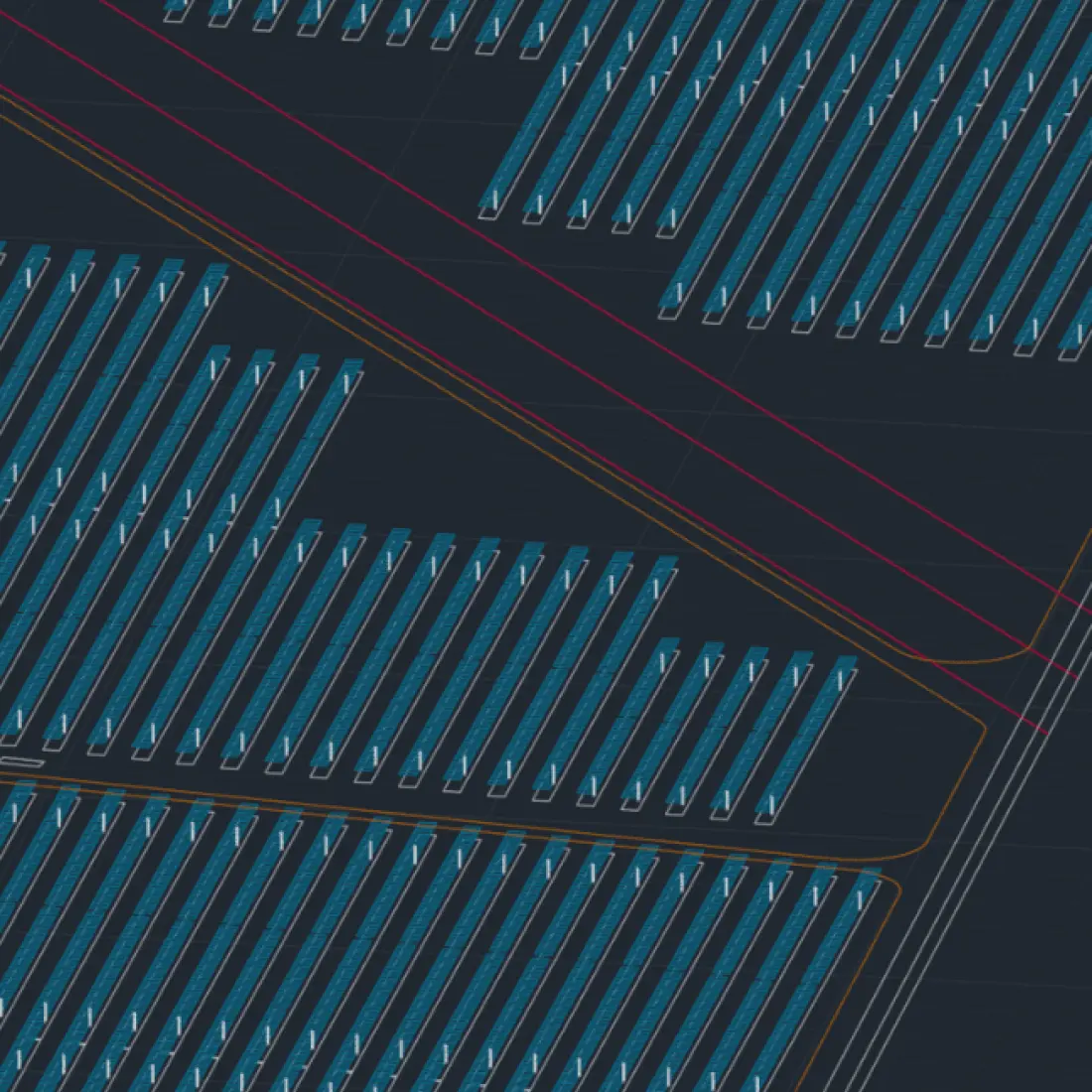
Integrates with PVcase Prospect and PVcase Yield
Seamlessly integrates with other industry-standard tools like PVcase Prospect and PVcase Yield, enabling comprehensive project analysis and continuation of work across project phases.


See it for yourself
Turn complexity into clarity and confidently move your data center project forward



![[EN]TOFU-Modern-site-selection-1200x518](https://hubspot-no-cache-eu1-prod.s3.amazonaws.com/cta/default/25919534/interactive-316375415996.png)