Agrivoltaics: the future of farming with solar power
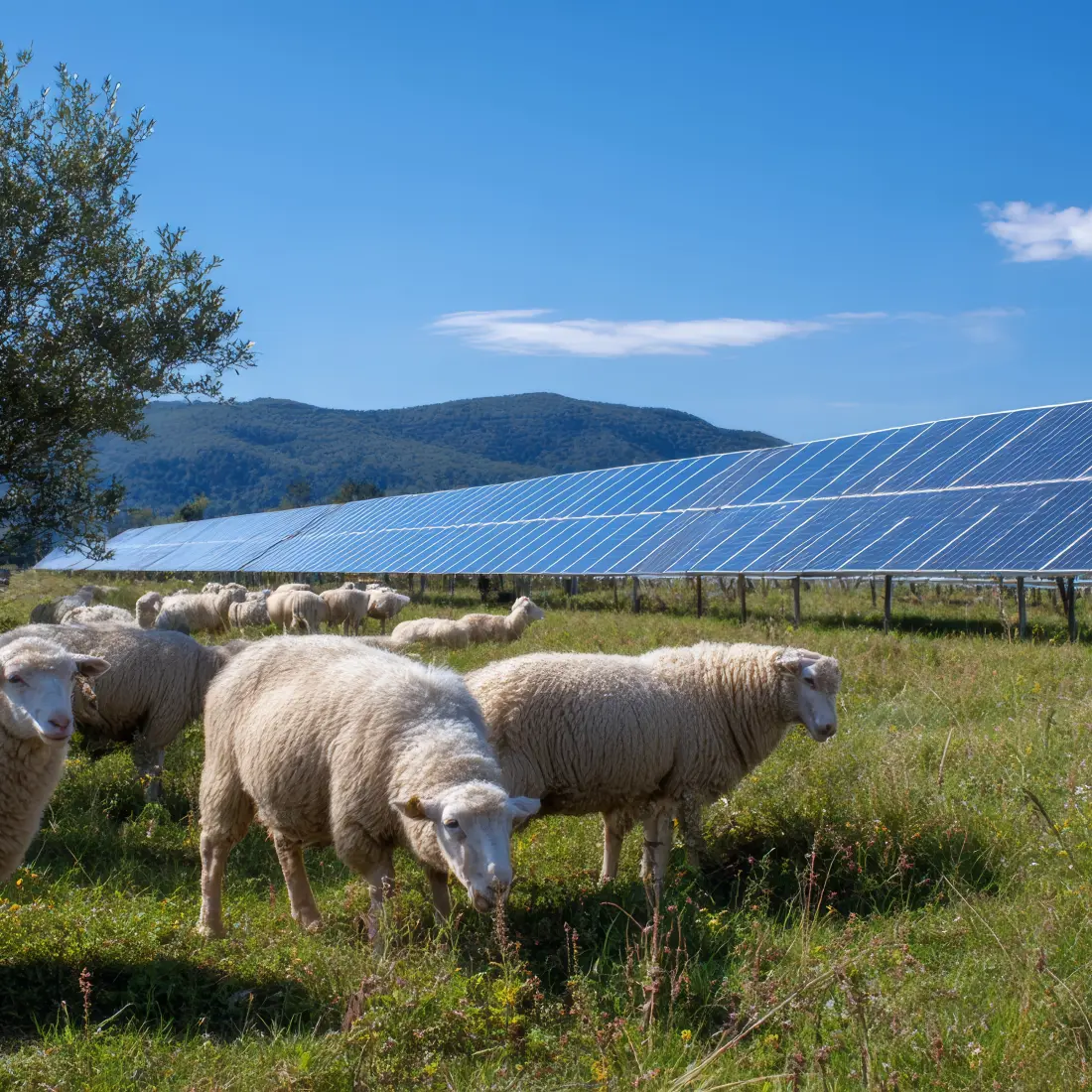


By 2050, 2.8% of the total territory in the EU is estimated to be used for solar energy. However, as the demand explodes, prime land for solar farms is getting harder to come by.
The best land for solar energy is flat, sunny, and accessible, while it is often the same land we rely on to grow food. Agrivoltaics system offers the best from both worlds – growing crops and generating electricity from the same patch of land.
Agrivoltaics has the potential to unlock synergies that tackle interrelated crises linked to human-made climate change: the decarbonization of our energy system, the need to transition to a more sustainable agricultural system, stopping and reversing biodiversity degradation, and supporting rural communities with high-quality jobs.
PVcase solutions, such as PVcase Ground Mount, are already being used to design and optimize agrivoltaic projects around the world. In this article, we’ll dig into how agrivoltaics works and how PVcase can enable an engineering of an optimal agri-PV project.
What is agrivoltaics?
Agrivoltaics, or agri-PV, is a land-use concept that colocates PV installations and energy generation, with agriculture and nature conservation, which are dependent on sunlight. Agrivoltaic systems should ensure that agricultural activity is at least preserved, and ideally improved by the presence of a PV system.
Many agrivoltaic applications are based on pretty standard ground-mounted setups, which can be easily designed in PVcase Ground Mount, in combination with:
Animal husbandry: traditionally combined with sheep farming, this set-up provides the advantage of saving on OPEX to cut grass on-site. Whereas sheep have been an ideal animal to cultivate on solar sites, goats are highly discouraged as they tend to climb on panels, potentially cracking them.
Crops between rows: a more novel approach to growing crops between the rows of a ground-mount system, usually with a larger space between the rows
Several alternative applications exist:
Elevating ground-mounted systems: elevated structures allow higher-growth crops, like fruit orchards, to be grown under PV systems with tracking and static systems. Reinforcing the structure opens up additional animal husbandry, such as cattle farming.
Vertical ground-mounted systems: agri-PV can also be mounted vertically on farm fencing to capture light from both sides and don’t interfere with fieldwork.
Crops and ground-mounted systems: interleaved systems, where agrivoltaic panels are spaced out so crops can grow between them.
Solar greenhouses: agri-PV panels are laid on the roof of barns or greenhouses. Semi-transparent PVs can provide an environmentally friendly energy supply while filtering sunlight necessary for growing crops.
Why is agrivoltaics important?
Agrivoltaic systems are emerging as a practical and innovative response to some of the toughest challenges facing agriculture today – climate change and land competition.
As climate change puts increasing pressure on crop yields through heatwaves, droughts, and unpredictable weather, agricultural PV offers a way to protect food production while generating clean energy.
At the same time, it helps ease the growing tension over land use, balancing the need for renewable energy infrastructure with the importance of preserving arable farmland.
Surveys in the U.S. show that over 80% of people are more likely to support solar projects if they’re paired with agriculture. At the same time, the usage of agrivoltaics could ease siting restrictions that often slow down solar projects.
Agrivoltaic systems can produce renewable electricity, but also manage to protect crops and animals from extreme conditions and support more sustainable farming methods. A pasture-based agrivoltaic system has been shown to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by nearly 70% compared to conventional farming and solar done separately.
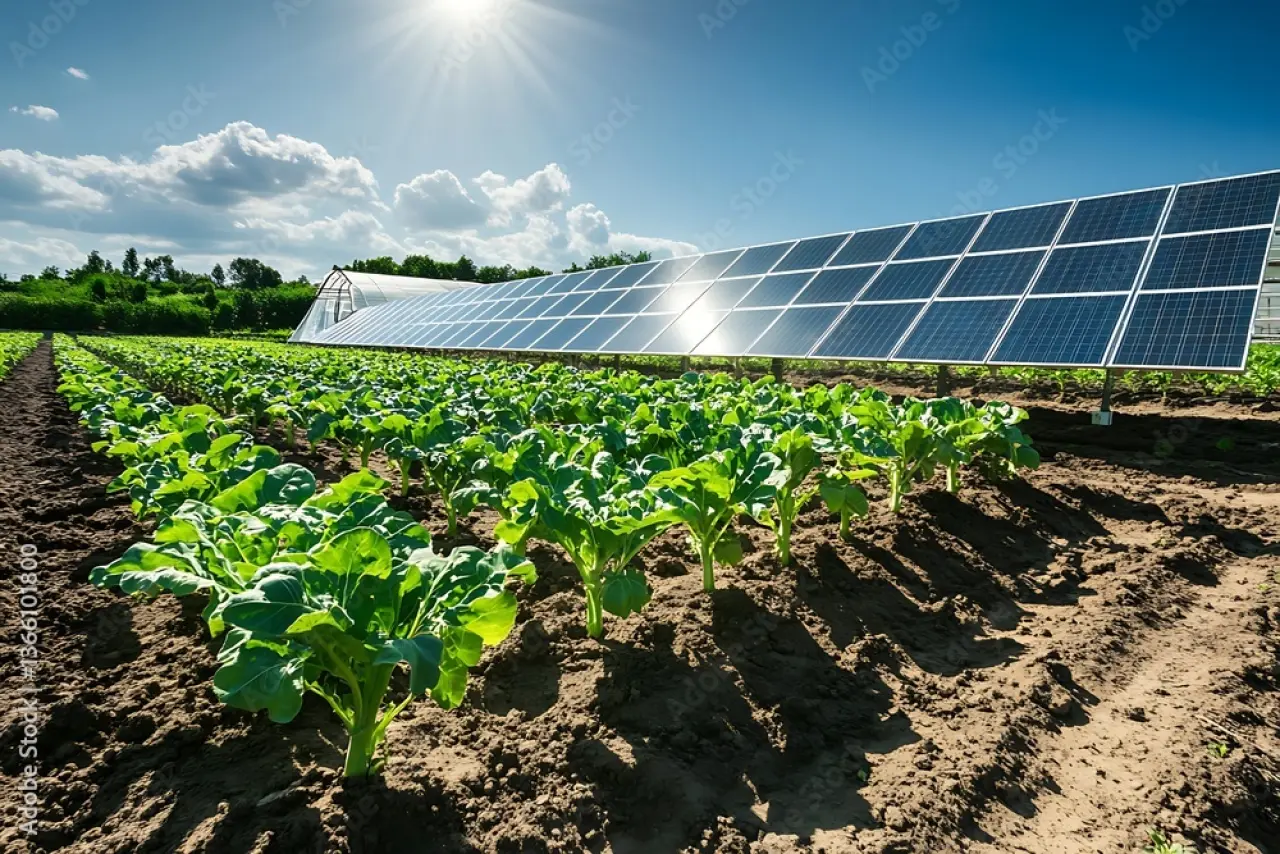

Agrivoltaics' benefits for agriculture
Agricultural solar energy provides key benefits to support the development of sustainable agriculture, including the reduction of environmental impacts of agriculture, increasing land productivity, improving water efficiency, enhancing biodiversity, reducing the need for agricultural plastics, and supporting socio-economic development in rural areas.
The biggest benefit of using solar panels in agriculture is increased productivity. Primarily, the shade from the panels can cut down on heat stress and keep soil temperatures more stable.
Panels also act as a natural barrier against wind, heavy rain, and hail, smoothing out the growing environment. Research shows that air temperatures stay stable under the panels, but the soil and plants remain cooler than in an open field. This protects crops from heat damage during critical growth stages.
So far, the results on the ground have been more than promising. Farms using solar panels for agriculture are seeing higher yields across various crops, from leafy greens like spinach and lettuce to broccoli, celery, and tomatoes.
Corn, wheat, and potatoes have also shown yield gains in some agrivoltaics farming trials. Strawberries, chili peppers, and pasture grass have also benefited from the microclimate created by agri-PV setups.
In Australia, extra shade provided by agri-PV systems helped sheep produce more and better-quality wool. Other research showed that agri-PV panels did not affect dairy production or cow behaviour. Still, the animals got shade during the hottest time of the day, which reduced their body temperatures.
Water is another major win. In arid zones like California and Arizona, experiments have shown that agrivoltaics can cut water evaporation by 14–50%, meaning that plants grown under agri-PV panels can survive on less irrigation. Agrivoltaic panels can condense moisture overnight, keeping grass and pasture lands hydrated even without rainfall.
What are agrivoltaics' economic and social benefits?
Installing solar power for agriculture could benefit rural communities. According to early simulations, agrivoltaic farming can boost land-use efficiency by 60–70%. Research found that when shade-tolerant crops are grown under solar panels, the farm delivers over 30% more economic value than conventional farming alone.
Another study states that putting solar panels and agriculture on the same land could help farming operations stay financially viable while reducing ecological impacts. It also enables farmers to diversify their revenue sources while lowering farm energy prices.
What are agrivoltaics’ disadvantages?
Despite its promising potential, solar power for agriculture is still navigating some challenges. High upfront costs, technical challenges, and limited public awareness still hold the field back. Bringing the agrivoltaics project from concept to reality involves careful planning of technical details, defining farm-specific needs, and complying with regulations.
Most agrivoltaic farming setups work best with shade-tolerant plants. However, sun-loving crops might struggle without modifications. Taller crops need higher panels, increasing material costs and structural complexity. The challenges for projects involving livestock multiply, as animals can damage panels or support structures.
One of the biggest challenges for agrivoltaic adoption is the limited range of equipment specifically designed for agri-PV setups, especially when it comes to flexible mounting systems or tools. Also, the initial setup price is high.
Navigating regulations could also be tricky. Different countries have inconsistent rules around agricultural PV, which can complicate the process of receiving a permit.
The question of the solar heat island effect also occasionally pops up in agri-PV debates. The concern is that large-scale agri PV installations might raise surrounding land temperatures. However, current research results are mixed, with some studies reporting minor warming and others showing negligible impact.
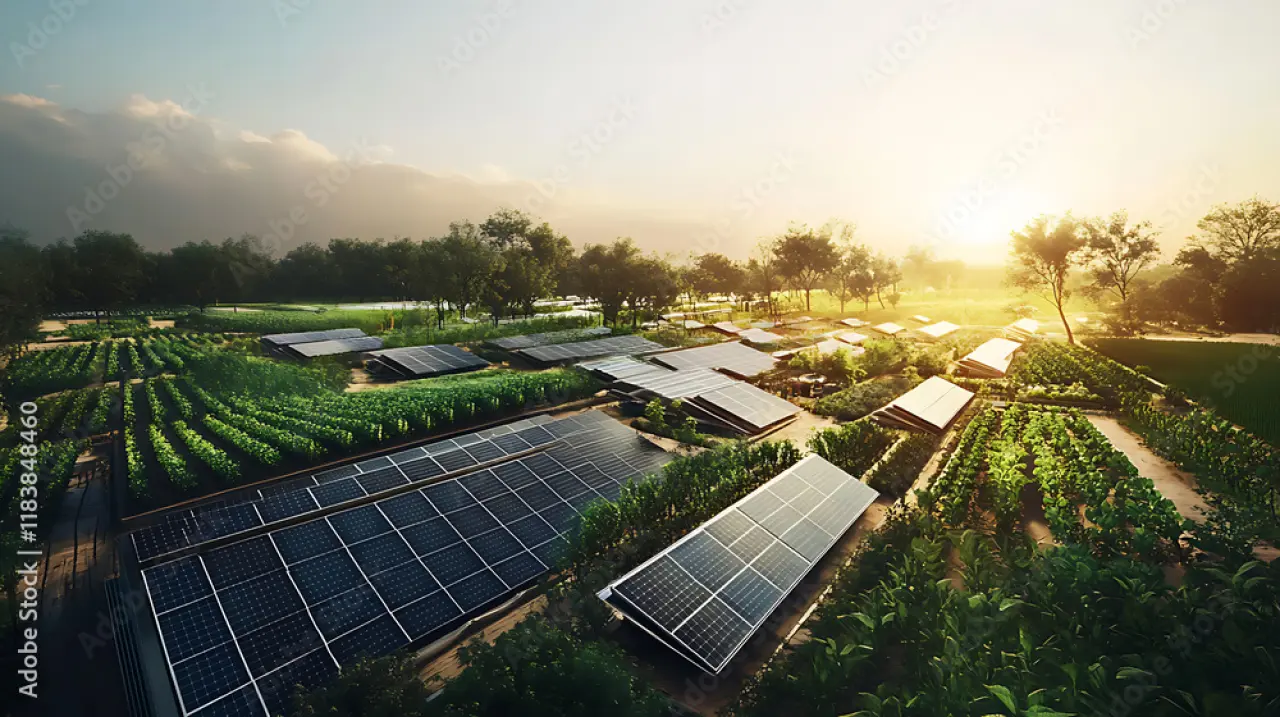

How can PVcase optimize the agrivoltaics system setup?
Designing a functional agrivoltaics system means balancing two different needs – productive farmland and high-efficiency solar output. That’s where the PVcase platform shines.
With nearly 80% of solar projects facing challenges, PVcase moves them towards the finish line providing a full suite of tools tailored for even the most complex agrivoltaic setups.
The PVcase Prospect solution streamlines site selection for agrivoltaic projects, automating the process to save time and reduce guesswork.
Once a site is chosen, PVcase Ground Mount lets users model their agri-PV systems with precision, and PVcase Yield provides in-depth productivity analysis to ensure the design delivers both energy and agricultural value.
Customizable ground-mount designs: flexible configurations suit different agrivoltaic models, from wide-row spacing for crops to elevated arrays for grazing.
Precise control over key parameters: adjust panel height, tilt, row spacing, and shading to meet the specific needs of different crops, machinery access, or livestock movement.
Optimization for agricultural conditions: enables modeling of site-specific conditions such as sunlight exposure, terrain, and soil use, maximizing both crop yield and solar output.
Topography-sensitive layouts: terrain data from Google Earth enables adaptive designs to adjust to uneven rural terrain.
Adaptable to multiple agrivoltaic setups: supports vertical bifacial systems, inter-row designs, and greenhouse-integrated PV.
Ensures compliance with local regulations: clear visualizations and detailed design data can support faster permit approvals.
As agrivoltaics continues to gain momentum, tools like PVcase are helping bridge the gap between ambition and execution. By streamlining planning, design, and analysis, the platform makes it easier to create efficient, site-specific systems that support both energy production and agricultural goals.


Start your agri-PV project with PVcase Ground Mount
Book a demo to learn more about PVcase platform and solutions