The Performance Ratio (PR) directly compares this theoretical potential with the real-world efficiency, making it one of the most valuable metrics for identifying underperformance. A difference is inevitable due to environmental and system losses, but a wider gap might indicate a deeper performance issue.
How to maximize solar panel efficiency
A comprehensive guide for commercial solar projects.
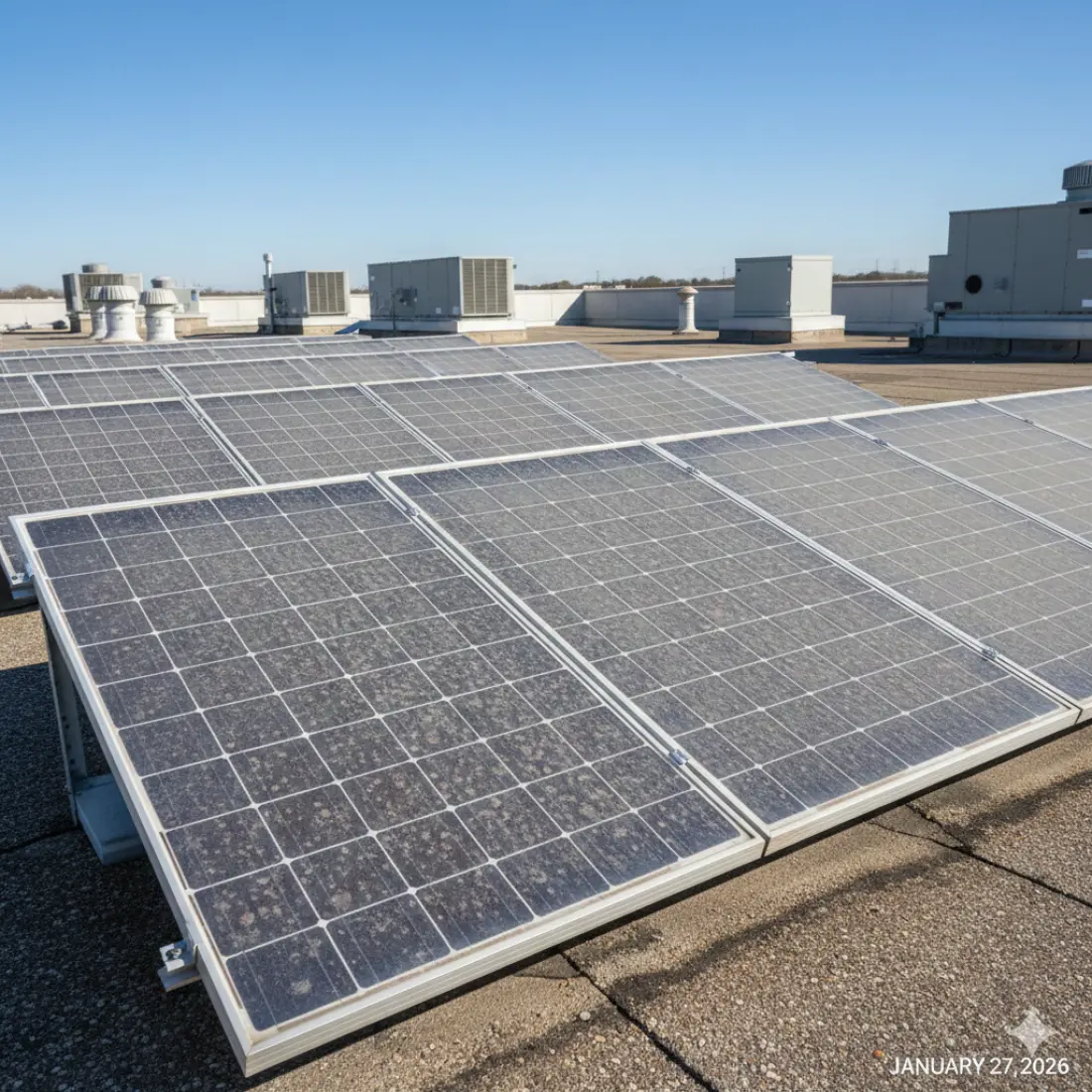


The definitive roadmap to achieving optimal solar performance for rooftop-based commercial solar projects.
Table of contents
- 1. Understanding solar panel efficiency fundamentals
- 2. Measuring and monitoring solar panel performance
- 3. Optimal solar panel orientation and placement strategies
- 4. Advanced solar panel optimization techniques
- 5. Maintenance and operational excellence
- 6. Implementing the right technologies for solar panel optimization
- 7. Conclusion: Implementing a comprehensive solar optimization strategy
Understanding solar panel efficiency fundamentals
Solar panel efficiency refers to the percentage of sunlight a panel can convert into usable electricity. It is calculated by dividing the electrical power output by the solar energy input under standard test conditions (STC), which is typically 1,000 W/m² of irradiance at 25°C cell temperature. A panel rated at 20% efficiency, for example, converts 20% of the sunlight hitting its surface into electrical energy.
Advances in solar panel optimization continue to defy what was previously considered feasible, with the top available brands setting benchmark efficiencies between 20-25%. This marks a significant improvement from the early days of commercially viable solar technology, when ~15% was the standard.
This increase in solar panel output efficiency is the result of decades of incremental advances in module technology, as well as an increasingly systematic approach to system efficiency. Both are critical for commercial developments where space is often limited, and demand is high.
And yet, many commercial solar installations still operate well below their optimal performance level. Poorly realized layouts, avoidable shading losses, and advanced degradation through non-optimized maintenance are among the factors responsible for an average of 5-15% in avoidable performance loss for commercial PV systems.
In this article, we will outline the key strategies needed - from optimal solar panel orientation to electrical design and ongoing maintenance - for a systematic approach to efficiency optimization. The end goal being a system that performs at its real world best.
Current efficiency standards and benchmarks for 2025
Efficiency standards continue to climb globally, reflecting continual improvements in cell technology and system design. As more advanced solar technology becomes widely available, it is important to consider not just how to maximize solar efficiency, but how to balance the cost-benefit ratio.
Monocrystalline panels, for example, might be setting the current benchmark for efficiency, but upfront costs can be prohibitively high. Commercial developments must look beyond potential energy per square meter and evaluate which investment point represents the highest cost-benefit for their buildable area, energy needs, and financial goals.
To ensure long-term reliability, performance, and standardization, standards such as the IEC 61215 and IEC 61730 ensure global compliance, while UL 61730 and UL 2703 largely govern commercial installations in the U.S.
Measuring and monitoring solar panel performance
Knowing critical KPIs, the factors that influence them, and how they translate to ROI is crucial for getting the most out of any commercial solar project.
What determines solar panel efficiency in commercial applications
Solar modules are first tested under standardized conditions to determine maximum energy generation potential (Watt peak). However, real-world performance is always lower than theoretical performance, largely due to environmental and system-level factors.
The distinction between theoretical module efficiency and practical system efficiency is an important one to make: module efficiency refers to the panel’s ability to convert sunlight at the cell-level, while system efficiency refers to the performance of the overall installation, including cabling, shading, orientation, and interconnection.
There are several factors that impact the efficiency of all solar installations, but are especially applicable to rooftop systems.
The first is shading from HVAC equipment, skylights, and surrounding buildings, which can be harder to accommodate for when compared to large-scale ground-mount systems.
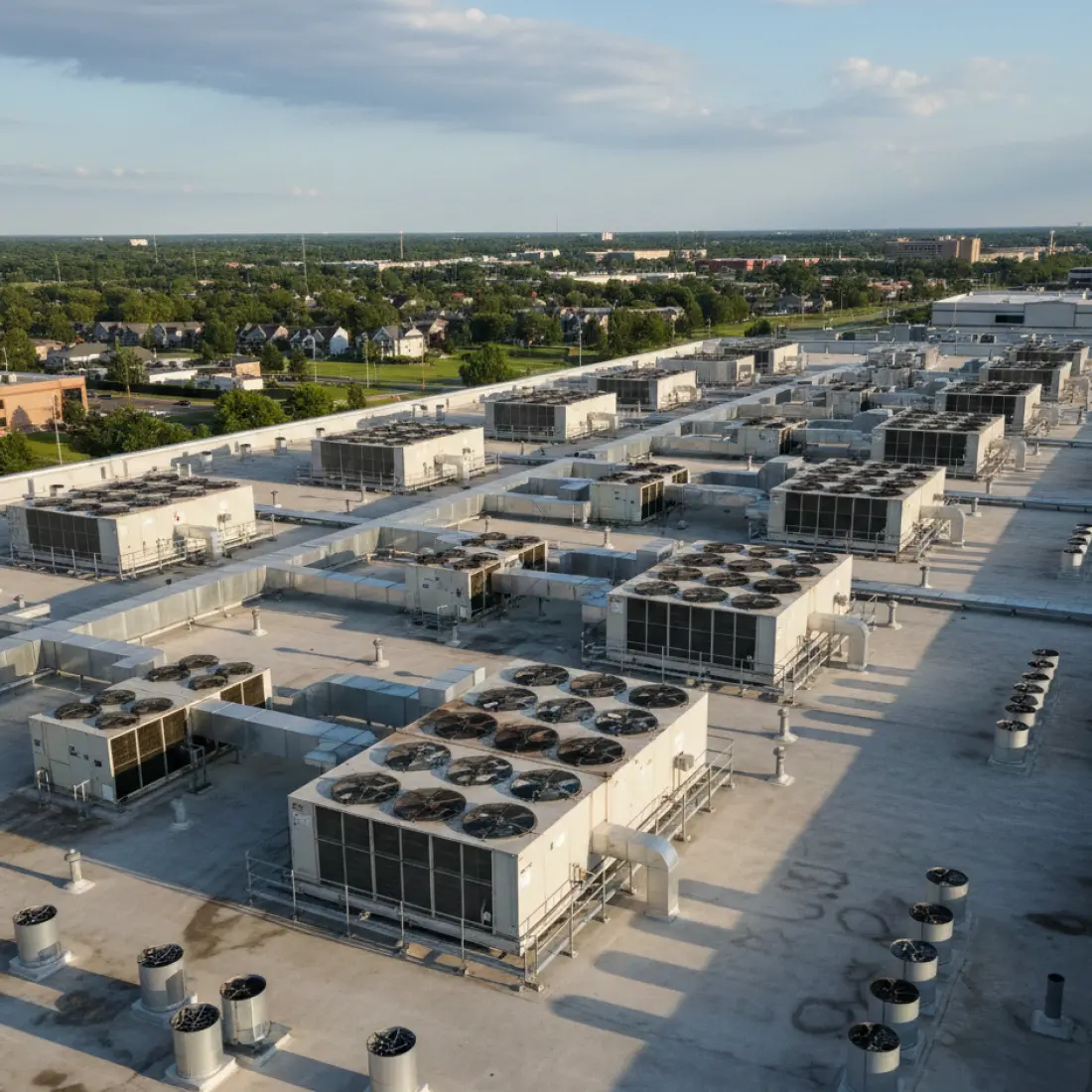

There is also temperature loss output to consider, particularly relevant in rooftop installations with limited airflow or other passive cooling options.

Finally, system-level degradation can range from around 0.5% to 1% each year. While degradation is inevitable of any system, it can be more pronounced in complex rooftop systems where regular maintenance is harder to perform.

More helpful than Watt peak or benchmark efficiency for evaluating true system optimization is the Performance Ratio (PR), as outlined above. This metric helps developers and customers who want to understand exactly how to maximize solar panel output.
ROI optimization through efficiency maximization
The Levelized Cost of Energy (LCOE) is a crucial measurement to quantify the financial success of a commercial solar investment.
By factoring CAPEX and OPEX costs, businesses can see clearly how their investment translates to cost per kWh, while system developers can use it as a foundational metric for project evaluation.
Beyond project optimization, LCOE can be further improved by taking advantage of all applicable tax benefits and incentives available for renewable energy, such as the Investment Tax Credit (ITC) or Production Tax Credit (PTC).
Finally, well-maintained systems are more likely to hold higher resale value and offer more dependable asset management profiles, making efficiency a key driver of short and long-term ROI.
Optimizing solar panel efficiency in commercial products starts with getting the orientation, placement, and tilt angles right. Together, these factors are instrumental in shaping real-world output.
Optimum solar panel orientation for maximum energy output
South-facing orientation has generally been considered the gold standard throughout the Northern Hemisphere for a long time now. However, a new approach to optimal solar panel placement is starting to gain traction, particularly for commercial rooftop projects.
East-west orientation is being increasingly embraced as a way to generate more consistent power throughout the day, beyond the midday peak. While this might not be the optimum solar panel orientation for maximum energy, the consistent generation better reflects real-world usage, and the dual-directional placement better utilizes space.
Even if an east-west placement is not possible or preferred, commercial systems can usually tolerate 10-30 degrees of deviation with minimal losses, allowing designers to optimize layouts around obstacles, as well as seasonal and regional weather variations.
Optimal solar panel placement considerations for commercial buildings
Optimization strategies can vary widely depending on roof type and site-specific constraints.
Pitched roofs can limit tilt options and demand careful roof-structure alignment, a challenge compounded by often difficult access conditions.

Flat roofs, on the other hand, allow for more flexibility when it comes to tilt and alignment, but often feature more obstacles like parapets, fire escape routes, and HVAC systems.
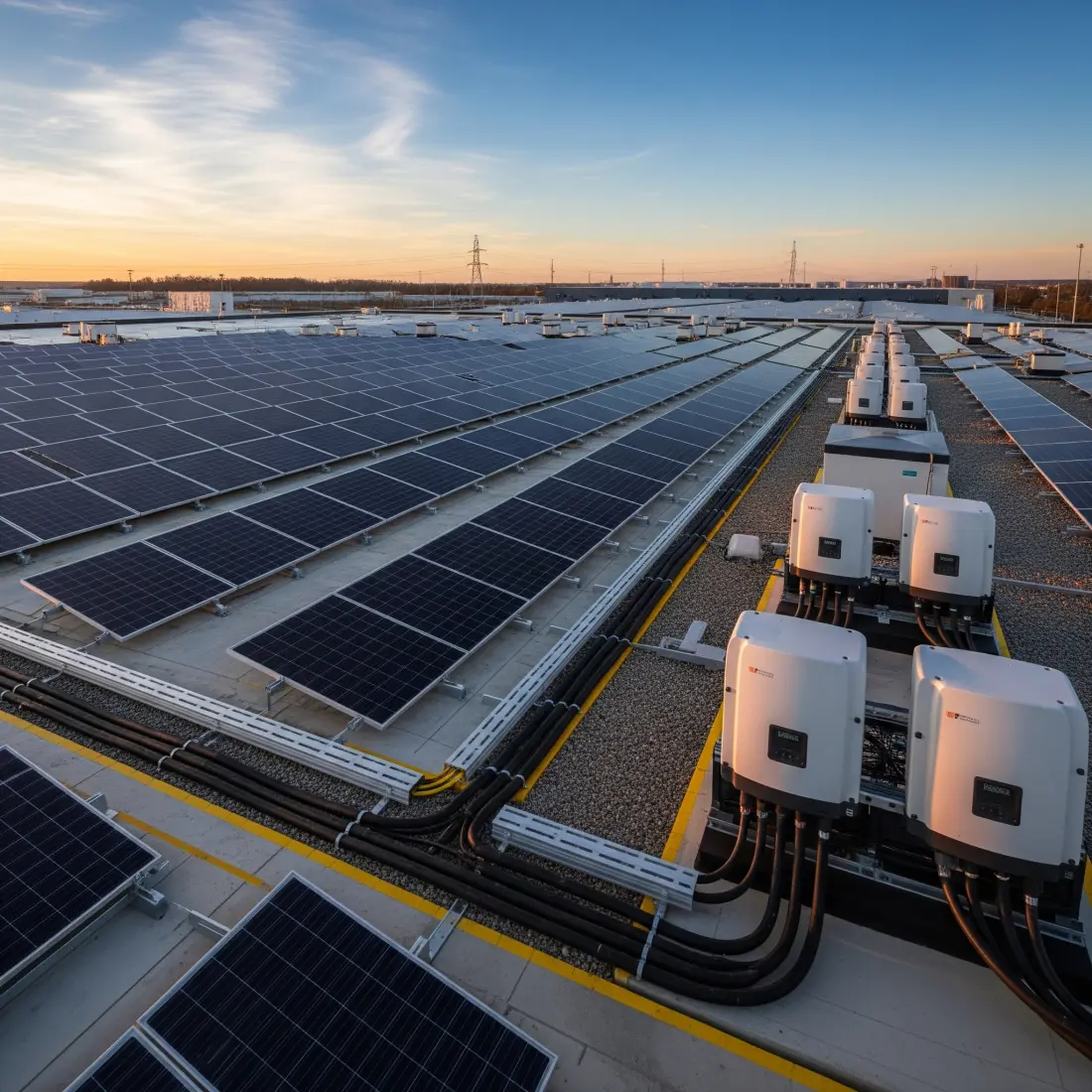

Regardless of roof type, engineers must consider extensive safety and regulatory requirements, as well as how best to optimize solar panels. These include compliant maintenance access, fire safety codes dictating setbacks, pathways, and spacing, and regulated integration with any existing building infrastructure.
Learn more about how to design PV systems on complex roofs.
Tilt angle optimization based on geographic location
Optimizing tilt angle is one of the best ways to maximize solar panel efficiency. While a tilt angle approximate to a site’s latitude can be a reasonable starting point, flat roof installations often favor a lower angle (5-15 degrees) for increased module density and reduced wind load.
Today, advanced yield optimization tools such as PVcase Roof Mount automate much of the simulation modeling required to optimize solar panel placement and tilt. That includes considering spatial constraints, near and far shading, and seasonal variations.
Ultimately, the optimal tilt is the one that balances energy yield with installation practicality for the best energy-to-cost ratio.
Advanced solar panel optimization techniques
Once the layout fundamentals are in place, advanced optimization techniques can unlock even greater efficiency gains and long-term value for commercial operators.
Increase solar panel output with monitoring and analytics
Real-time monitoring systems provide visibility into real-world performance and help to identify areas for further optimization, as well as diagnose potential issues.
Advanced platforms can track an array of key indicators such as energy yield, inverter output, PR ratio, system availability, and degradation trends. This level of oversight allows for predictive maintenance planning, allowing operators to identify and fix problems before they become significant.
Supporting predictive analytics, remote monitoring, and automatic alerts minimize downtime with immediate notifications, while also reducing operational expenditure through automation.
Over time, an integrated data approach allows operators to maximize not just solar panel efficiency, but maintenance and uptime too.
Optimize solar panels using smart inverter technology
Smart inverter technology is playing a growing role in commercial solar optimization. Namely, Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT), capable of continually adjusting operating conditions to accommodate for changes in irradiance and temperature.
More granular optimizations can be implemented in systems with panel-level controls, ideal for complex topographies or shading patterns.
Finally, evolving support for reactive power control and smart grid integration capabilities are enabling systems to operate more efficiently while streamlining grid tie-in and compliance.
Maintenance and operational excellence
Once a system design has been fully optimized and installed, the focus then shifts toward maximizing long-term performance through disciplined maintenance and oversight.
Regular cleaning and maintenance protocols
Soiling is one of the most common causes of solar underperformance. Depending on the climate and location, going without regular cleaning can reduce output anywhere from 5% to 30%.
Optimal cleaning frequency will depend on the local conditions. Particularly dry climates often mean rapid dust accumulation, as do active industrial zones or high-traffic urban areas.

Ultimately, maintenance cycles, as well as other considerations like whether it is better to invest early in an automated cleaning system or pay for regular professional cleaning, will depend on the cost-benefit analysis of each development.
Performance monitoring systems for commercial solar
As the solar market continues to grow, so too does the demand for future-proof solutions to ongoing maintenance and monitoring.
Commercial systems are now more commonly deploying similar string-level, inverter-level, and even panel-level monitoring systems as those found on large- to utility-scale projects.

By integrating these monitoring systems into existing building management systems (BMS), and even dedicated apps and mobile dashboards, benchmarking real-time performance against expected values is simpler than ever.
Identifying and addressing efficiency loss factors
While the unexpected can and will happen, commercial systems also face a largely predictable set of loss factors that should be proactively managed for ongoing solar panel optimization.
Common issues include evolving shading patterns, wiring faults, and dirt accumulation. If not properly dealt with, these issues can lead to the localized development of hot spots, defective cells that become a power drain rather than a provider.
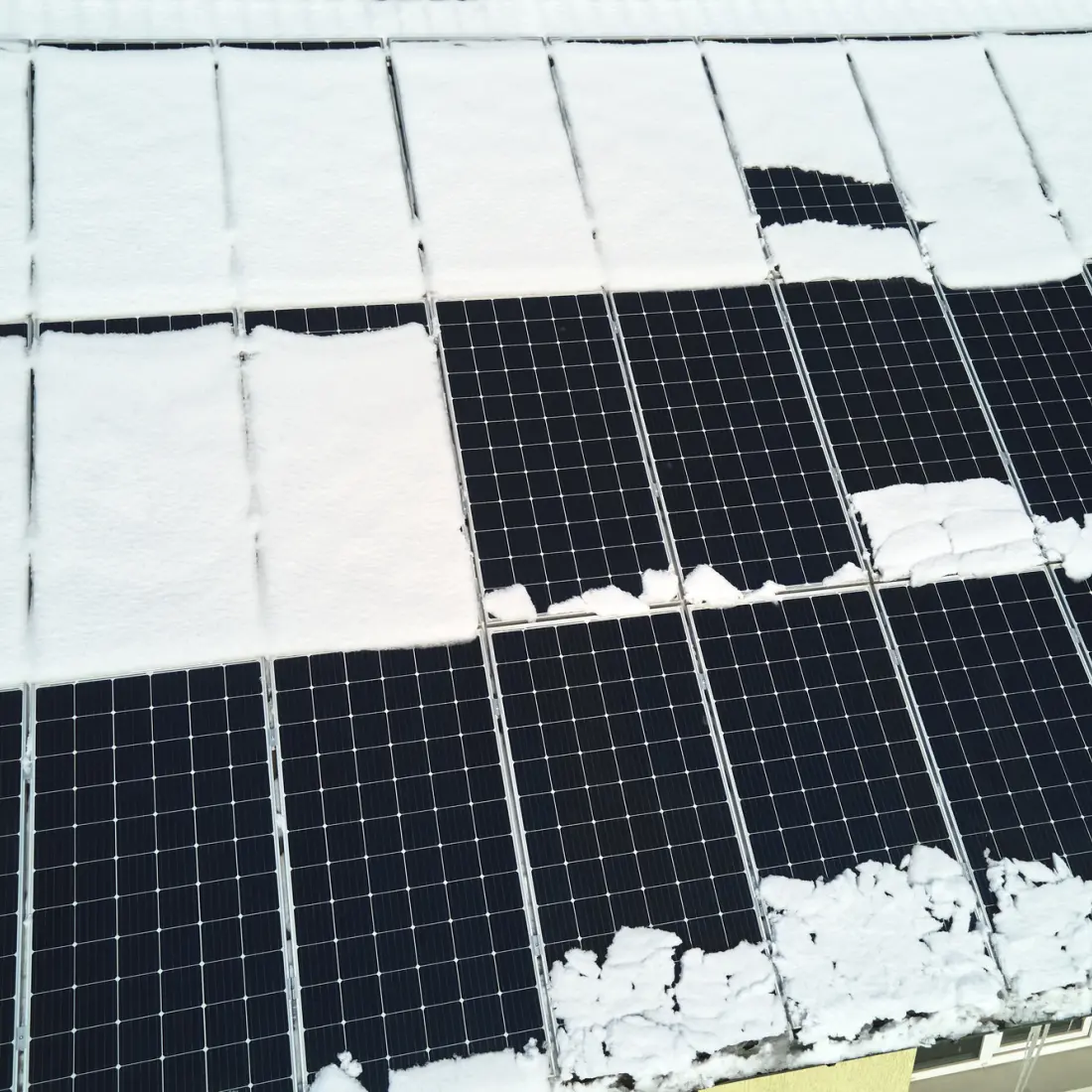

Being able to differentiate between normal signs of degradation and abnormal performance declines is essential to ensuring potential loss factors are addressed before they become a major problem.
Implementing the right technologies for solar panel optimization
As commercial systems grow more sophisticated, advanced technologies like bifacial modules, digital twin planning, and automation offer enticing opportunities to further optimize development efficiency and long-term performance.
Bifacial solar panels and tracking systems
Bifacial solar panels can produce power from both of their sides, meaning they can also absorb light reflected off the ground or roof for increased solar panel output. They are particularly effective on highly reflective surfaces such as white or light-colored rooftops.
However, benefits depend heavily on specific shading conditions and installation angles, so whether they are worth the additional investment is dependent on the use case.

Beyond the panels themselves, it is important to consider whether a fixed-tilt or single-axis tracker is the better investment. While utility-scale single axis trackers can deliver 20-30% more energy than fixed-tilt systems, the returns are often diminished for commercial rooftop projects. Restricted rooftop space, higher initial costs, increased maintenance requirements, and additional structural demands can significantly shift the LCOE calculation against trackers.
Often, the smarter cost-benefit strategy for a commercial project is a systematic approach to maximizing rooftop potential using the simplest system needed.
Digital twin technology and yield optimization
The emergence of digital twin technology has been a game-changer for the PV industry.
With the ability to now simulate real-world conditions to a remarkable degree of accuracy, simulation tools like PVcase Yield are transforming the way we approach yield optimization.
Advanced solar development platforms help designers understand how to maximize solar panel efficiency through rapid simulation running, automated and iterative design processes, and granular data layers such as predictive weather and climate forecasting.
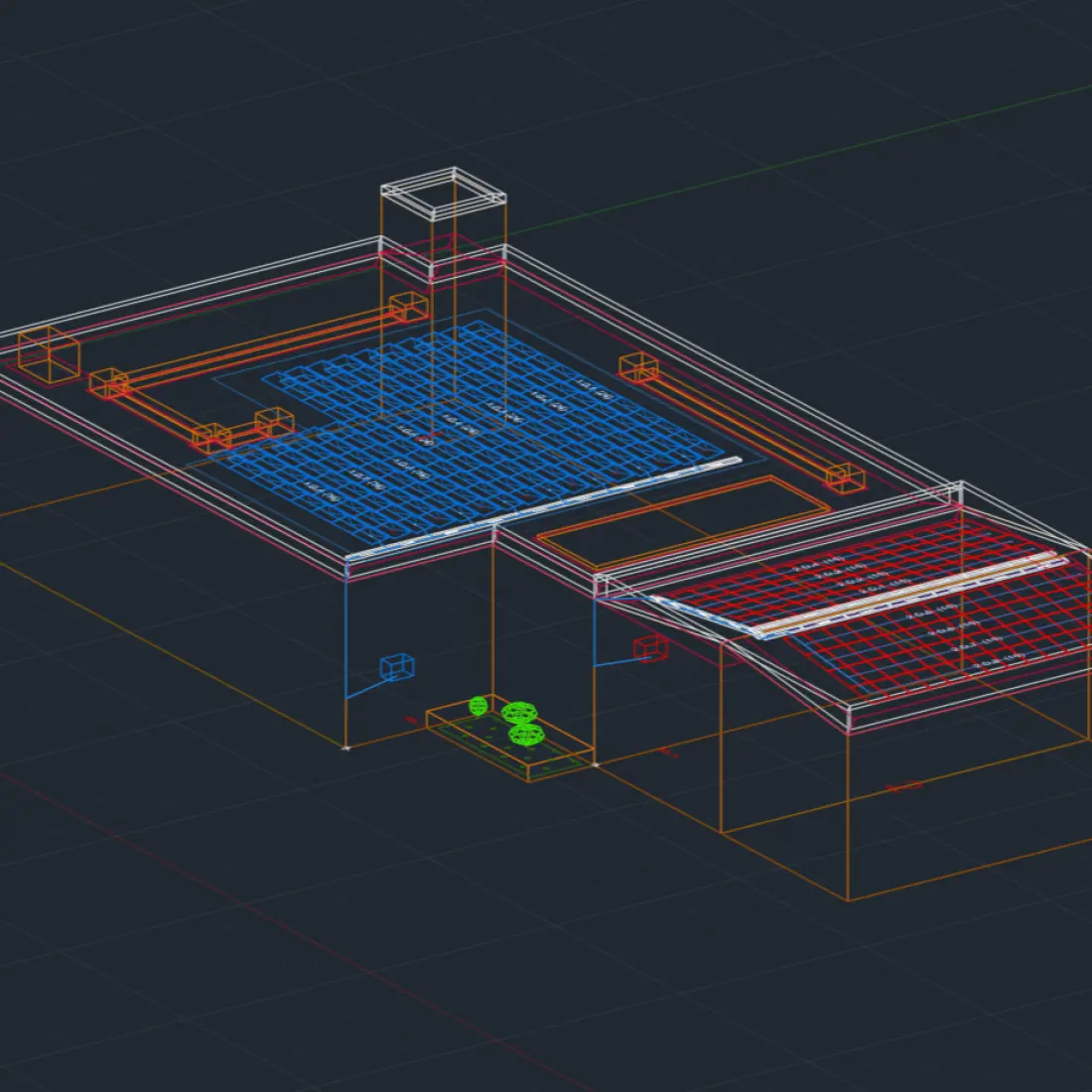
The PVcase solution for maximum solar efficiency
PVcase Roof Mount is the efficient solution for C&I rooftop design. By automating previously labor-intensive tasks such as electrical calculations, cable routing, and shading analysis, engineers can expect design time to be reduced by up to 85%.
In addition to time saved, error-free layout generation, factoring load and spatial constraints, minimizes production costs through optimized placement, and delivers stronger long-term ROI.
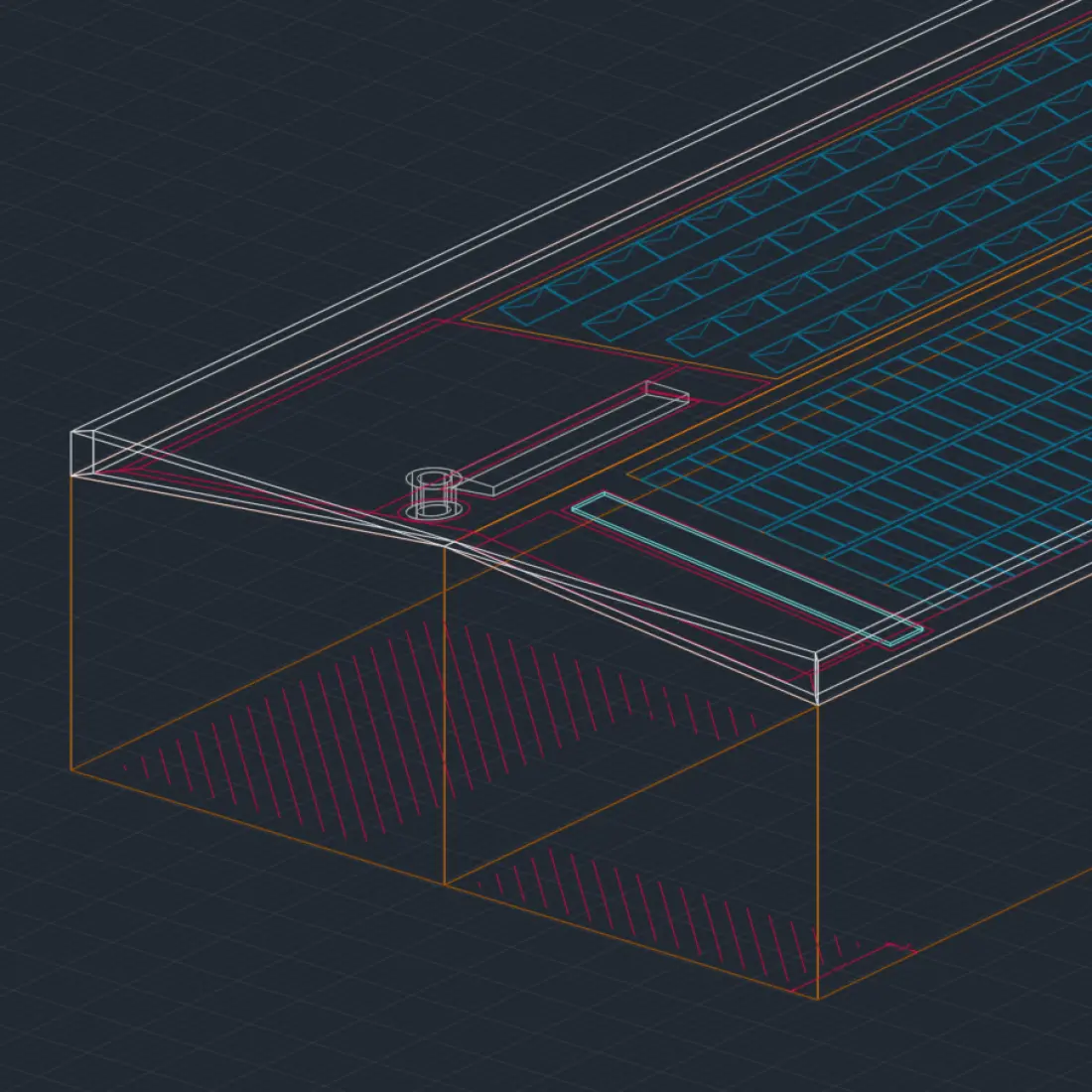
Conclusion: Implementing a comprehensive solar optimization strategy
Solar panel and system optimization demands a holistic approach that means balancing intelligent design with smart investments in the right technology. Beyond the initial investment, ongoing optimization depends on continuous monitoring and disciplined maintenance.
A phased implementation plan, starting with system design optimization, followed by monitoring enhancements, and finally predictive maintenance, can help commercial organizations to prioritize investments while managing expenditure.
Every stage of development, from pre-planning to active construction and post-management, can be supported by advanced automation and development tools like PVcase. With precise modeling, accelerated workflows, and unified environments, projects can slash delivery times while ensuring optimal solar efficiency.
For more, discover our free eBook on how to implement PVcase Roof Mount in your next project, or contact our team today for a free, personalized demo.


Try PVcase now
See our AutoCAD-based solar design software in action and learn how it can benefit your business. PVcase leverages automation, a high level of precision, and intelligent algorithms to improve the efficiency, accuracy, and quality of PV designs.
![[EN]pvcase-resources-the-state-of-solar-project-development-report-CTA-1200x518](https://hubspot-no-cache-eu1-prod.s3.amazonaws.com/cta/default/25919534/interactive-272771778795.png)